Laboratory Astrophysics
Laboratory Astrophysics
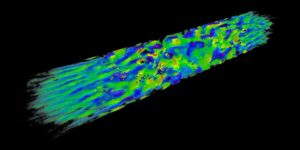
Our group is engaged in different imaging tools for electron density retrieval in the X-ray regime at poly- as well as monochromatic sources. We are looking for potential applications of X-ray phase-contrast and dark-field imaging on plasma physics especially with regard to the field of laboratory astrophysics (see e.g. testing of shock waves in the laboratory, Figure 1). In collaboration with plasma physics groups the developed imaging tools can be tested at real and simulated plasmas. We aim at the observation and the analysis of dynamic processes of laser-shocked plasmas.
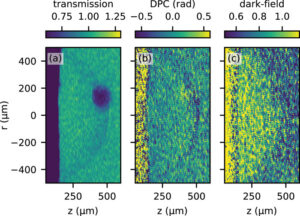
Recently, we investigated the propagation of homogenisaion in foams of very low density. The process was detectable only by the X-ray dark-field image which lead to a measurable signal caused by the microstructure of the foam (Figure 2). The homogenisation disturbs this structure which leads to a measurable decrease in the dark-field signal.
Publications:
- L. Wegert et al., 2024, Matter Radiat. Extremes, Vol. 9, No. 4 (https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0200440)
- A. Wolf et al, 2022 J. Synchrotron Rad., 29, 794-806 (https://doi.org/10.1107/S160057752200193X)
- S. Schreiner et al, 2021, J. Imaging 2021, 7(9), 178 (https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging70901781)
- B. Akstaller et al, 2021 JINST 16 P06021(https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-0221/16/06/P06021)
- A. Wolf et al, 2020, Opt. Express 28, 13553-13568 (https://www.osapublishing.org/oe/abstract.cfm?uri=oe-28-9-13553)
- M. Seifert et al, 2020, J. Imaging 6(7) 63 (https://www.mdpi.com/2313-433X/6/7/63/htm)
- M. Schuster et al, 2019, JINST 14 P08003 (https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-0221/14/08/P08003/meta)
